Programming in Java
Object Oriented in Java
Advanced topics in Java
 Tutorials
Tutorials

C is a very powerful and widely used language. It is used in many scientific programming situations. It forms (or is the basis for) the core of the modern languages Java and C++. It allows you access to the bare bones of your computer.C++ is used for operating systems, games, embedded software, autonomous cars and medical technology, as well as many other applications. Don't forget to visit this section...
String Handling
In java, String is a predefined class that is final, so string objects are used and that may be the combination of array of characters. String variable is declared as following :
String name="Sharp Tutorial"; // also known as string literals
We can also create string objects with the help of “new” keyword as following :
String n= new String ("Welcome String"); If we use string literals, then in the following example ,
String name="Sharp Tutorials";
String name1="Sharp Tutorials"// here another instance not created as same string is present in string pool.
⇒ If we create two objects with new keyword, then two different objects are created.
Some important functions that may be called on String are as following :
1. equals(String s) :
This function compares if two string are equals or not.
3. length() :
This function returns the length of the string.
5. indexOf(char ch) :
This function returns the index of the given character.
7. trim() :
this function removes the leading and trailing whitespaces.
9. contains(String s) :
It returns true or false if a given string is found in the string.
2. equalsIgnoreCase(String s) :
This function also returns true or false and when comparing two strings, it ignores the case (upper/lower).
4. charAt(int index) :
This function returns the character at the given index.
6. lastIndexOf(char ch) :
This function returns the last index of the given character.
8. substring(int beginIndex, int lastIndex) :
This function cuts a portion of the String, if only one index is being passed, then the string is cut till the end from the given beginning Index.
10. toUpperCase(), toLowerCase() :
this function converts the string in upper case and lower case respectively.
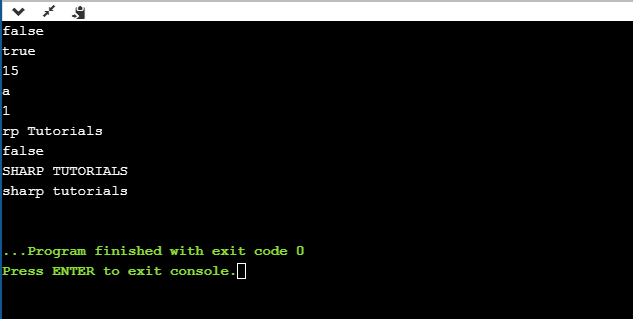
String programm :
class StringExamples
{
public static void main(String argsp[])
{
String name="Sharp Tutorials";
System.out.println(name.equals("sharp tutorials"));
System.out.println(name.equalsIgnoreCase("sharp tutorials"));
System.out.println(name.length());
System.out.println(name.charAt(2));
System.out.println(name.indexOf('h'));
System.out.println(name.substring(3));
System.out.println(name.contains("tuts"));
System.out.println(name.toUpperCase());
System.out.println(name.toLowerCase());
}
} Output of the above program is as following :